Today's KNOWLEDGE Share
What are modified polyphenylene ethers?
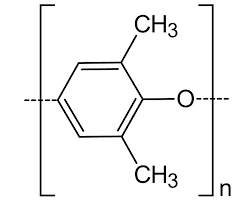
Modified polyphenylene ether (modified PPE or m-PPE) is the common name for a family of polymer alloys formed by blending modified polyphenylene ether (PPE) resin a type of non-crystalline engineering plastic with various other resins. PPE resin is a non-crystalline resin with a glass transition temperature around Tg=210°C; the primary molecular chains in this resin consist of benzene rings linked by ether bonds, making the resin highly resistant to hydrolysis.
PPE resin exhibits low water absorption and boasts a low specific gravity of just 1.06, the smallest of all general-purpose engineering plastics. PPE resin also has the smallest linear-expansion coefficient of all general-purpose engineering plastics, ensuring excellent dimensional stability. Other advantages of PPE resin include its superior electrical properties, including excellent dielectric permittivity and loss tangent over a wide frequency range. PPE resin is further distinguished by its outstanding resistance to acids and alkalis.
On the other hand, drawbacks of pure PPE resin include high molten-state viscosity making it difficult to mold into desired shapes and susceptibility to degradation in the presence of aromatic hydrocarbon-based solvents such as oils.
Modified polyphenylene ether is also called modified polyphenylene oxide (modified PPO or m-PPO). However, PPO is a registered trademark, and the generic name is PPE.
PPE resin is rarely used in its pure form, but is frequently blended with polystyrene (PS) or other resins to yield a wide variety of alloy materials. Alloys of PPE and PS can achieve complete solubility for arbitrary values of the PPE/PS constituent ratio, and this fact can be exploited to improve fluidity and cover a wide range of heat-resistant behavior, making PPE/PS among the most important of all polymer-alloy systems. PPE resins are also easily blended with non-brominated, non-chlorinated flame retardants to yield flame-retardant materials.
Additionally, PPE may be alloyed with materials such as polyamide (PA), polypropylene (PP), polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), or elastomers such as SEBS to yield new materials combining the above-noted advantages of PPE resins with the features of the various partner resins.
The process of alloying PPE resin with other resins to improve material properties is known as modification, and the resulting materials are known as modified PPE (m-PPE) resins.
source:Asahi kasei




No comments:
Post a Comment