Today's KNOWLEDGE Share
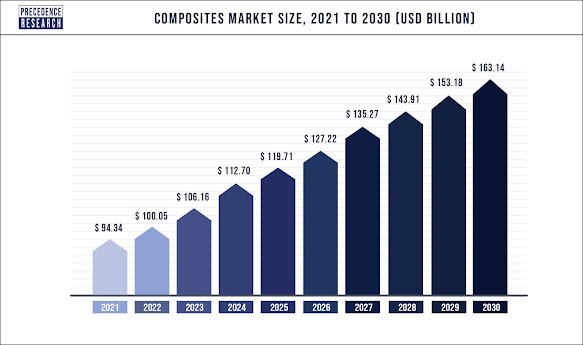
The global composites market size is expected to reach around US$ 163.14 billion by 2030!
Research conducted by Precedence Research shows that the global composites market size was valued at US$ 94.34 billion in 2021 and is expected to reach around US$ 163.14 billion by 2030, expanding growth at a noteworthy CAGR of 6.3% from 2022 to 2030!
Some of the main influencing factors of the composites market include proliferating requirement for lightweight materials in the #defense, #automotive and #aerospace sector, rising demand for chemical and corrosion resistance materials in #pipe & #tank and #construction field. Escalated development of cost effective #carbonfibers, rapid cure #resin system and improved performance glass fiber are some of the evolving trends that are positively affecting #composites market dynamics!
Among different product type segmentation, in 2021, #glassfiber appeared as a prominent segment and amounted for around 61.5% revenue share of the total market. This tremendous growth is attributed to its large demand in construction, electronics and electrical, wind energy and transportation sectors.
The automotive and transportation segment accounted for the largest revenue share of 21.5% in 2021. The outlook of the global composites market seems eye-catching with alluring prospects in numerous end-use sectors such as #windenergy, #electrical and #electronics, construction, pipe & tank, #marine, #transportation , #consumergoods, and aerospace among others. Transportation sector that includes #commercialvehicles, coaches, #buses and #automobiles, is projected to emerge as one of the major U.S. markets in the coming few years. At present several prominent vehicle manufacturers are spending in composite materials technology in order to decrease weight and address the targets of authorized carbon emission reduction.
Reference: Composites Market Global Market Size, Trends Analysis, Segment Forecasts, Regional Outlook 2022 - 2030, published by Precedence Research.
Source:#managingcomposites #thenativelab
Follow: http://polymerguru.blogspot.com