📢Time to Get Technical...📢
Let's learn more about BMC's! 👀
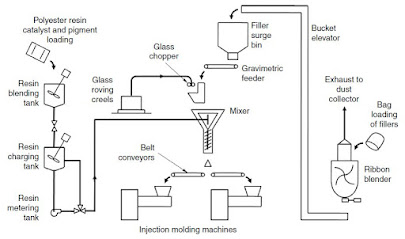
Bulk molding compound (BMC) is a bulky mixture of chopped glass fibers, resin paste, and fillers. Even though other fibers such as sisal, asbestos, carbon, aramid, chopped nylon rag, and wood are used, the most common reinforcing fiber in BMC is E-glass fiber. As BMC is usually mixed in a dough-like form rather than as a sheet, it is also called a dough molding compound (DMC) and is sold in a log or rope form. The resin formulation of BMC materials is similar to SMC materials. Chopped glass fibers are compounded with the resin paste in an intensive mixer and extruded in the form of a continuous log. The extruded log is cut to the desired length by a pneumatic cutter located outside the extruder.
The glass fiber content of BMC is generally 5∼10% lower than that of SMC, and the fibers are shorter (generally less than 25 mm). Therefore, the mechanical properties of BMC are lower than those of SMC. The impact strength is highly dependent on the fiber length. This improvement in the impact resistance by the increase in fiber length becomes less significant above the fiber length of 12.7 mm. Moreover, fiber lengths over 12.7 mm result in mixing and molding problems. Therefore, the fiber lengths of BMC seldom exceed 12.7 mm, and the most common fiber length is 6.23 mm. Sometimes, BMC is mixed at the molding location whereas it also can be purchased from commercial manufacturers that sell the material as a ready-to-mold premix.
This schematic of a continuous compounding system for BMC.
Bibliographical Reference:
Manufacturing Techniques For Polymer Matrix Composites - Page 57
Source:managingcomposites




No comments:
Post a Comment