The plastics machinery shipments in North America continued to increase in the third quarter according to the statistics compiled and reported by the Plastics Industry Association’s (PLASTICS) Committee on Equipment Statistics (CES).
Injection Molding & Extrusion Machinery Shipment
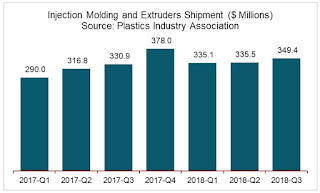
The preliminary estimate of shipments of primary plastics equipment (injection molding and extrusion) for reporting companies totaled $349.4 million in the third quarter. This was a 4.1-percent increase from the $335.5 million (revised) second-quarter shipment. Injection molding shipments in the second quarter were higher than previously thought. Year over year, shipments grew 5.6 percent.
Perc Pineda PhD, Chief Economist of PLASTICS, said:
“Plastics machinery shipments recovered in the third quarter following a weak second quarter. We expect higher shipments in the fourth quarter. We have a tight labor market and U.S. manufacturers, including plastics machinery manufacturers, have been working on production backlogs. As a result, shipments are pushed into the next quarters.”
Quarterly Statistics
- On a quarterly basis, injection molding shipments increased 2.1 percent. Single-screw and twin-screw extruder shipments continued double-digit growth of 23.8 percent and 14.2 percent, respectively.
- Compared to the third quarter last year, shipments of injection molding were up 4.6 percent. Shipments of single-screw extruders rose 7.7 percent and twin-screw extruders 17.2 percent over the same period.
Perc Pineda said:
“Except for soft auto and home sales numbers in the third quarter, the U.S. economy is still in expansionary mode—and that’s good news for plastics machinery manufacturing. While there are projections of moderate growth next year, it is expected that the U.S. economy will remain healthy.”
Source: Plastics Industry Association (PLASTICS)