Monday, December 31, 2018
Sunday, December 30, 2018
An eco-friendly vinyl hybrid resin made with zero styrene
Perma-Liner
Industries, the manufacturer and supplier of trenchless pipeline
rehabilitation equipment and materials in North America, is introducing a
eco-friendly resin called Perma-Liner vinyl hybrid resin.
“Our newest resin, the Vinyl Hybrid, has an array of benefits that are attractive to those looking for reduced labor costs, fast cure times and more,” said Rishi Vasudeva, business excellence manager at Perma-Liner. “This Resin is formulated with zero styrene – a potentially harmful substance per OSHA – allows it to be used in areas that would previously need to be evacuated due to the presence of styrene, such as schools, hospitals, churches, office buildings and more.”
The
vinyl Hybrid resin has a standard pot life of more than eight hours and
uses an easy initiator with one percent cumyl hydroperoxide (CHP) by
weight making it cheap, easy and effective. With this new resin, it can
be hot water or steam cured at a minimum of 140°F temperature held for
28 minutes with no post cure. The lower cure temperature of 140°F means
it’s safer, gentler on equipment, a short time to maintain the
temperature and easier temperature to reach for longer shots.
Perma-Liner’s vinyl hybrid boasts consistent viscosity and is resistant
to sag and draining around vertical surfaces and reinforcement.
Perma-Liner’s
newest resin joins the company’s other resins: the high-performance
vinyl ester, styrene-free silicate and the ever-popular 100 percent
solids epoxy.
Source:perma-liner
Tuesday, December 25, 2018
Scientists Discover Method to Produce FDCA Using Non-food Glucose Derivative
Scientists have discovered a novel method to synthesize
furan-2,5-dicarboxylic acid (FDCA) in a high yield from a glucose
derivative of non-food plant cellulose, paving the way for replacing
petroleum-derived terephthalic acid with biomaterials in plastic bottle
applications.
The chemical industry is under pressure to establish energy-efficient
chemical procedures that do not generate by-products, and using
renewable resources wherever possible. Scientists believe that if
resources from non-food plants can be used without putting a burden on
the environment, it will help sustain existing social systems.
In the study published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition, a Japan-Netherland research team led by Associate Professor Kiyotaka Nakajima at Hokkaido University and Professor Emiel J.M. Hensen at Eindhove University of Technology succeeded in suppressing the side reactions and producing FDCA with high yields from concentrated HMF solutions (10~20 wt%) without by-products formation. Specifically, they first acetalized HMF with 1,3-propanediol to protect by-product-inducing formyl groups and then oxidized HMF-acetal with a supported Au catalyst.
Conventional methods produce by-products making large-scale FDCA production difficult, while this new method yields FDCA efficiently without by-products formation.
About 80% of 1,3-propanediol used to protect formyl groups can be reused for the subsequent reactions. In addition, drastic improvement in the substrate concentration reduces the amount of solvents used in the production process.
Kiyotaka Nakajima says “It is significant that our method can reduce the total energy consumption required for complex work-up processes to isolate the reaction product.”
“These results represent a significant advance over the current state of the art, overcoming an inherent limitation of the oxidation of HMF to an important monomer for biopolymer production. Controlling the reactivity of formyl group could open the door for the production of commodity chemicals from sugar-based biomaterials,” says Kiyotaka Nakajima. This study was conducted jointly with Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation.
Source: Hokkaido University
Decreasing Burden on the Environment with Renewable Resources
The chemical industry is under pressure to establish energy-efficient
chemical procedures that do not generate by-products, and using
renewable resources wherever possible. Scientists believe that if
resources from non-food plants can be used without putting a burden on
the environment, it will help sustain existing social systems.
It has been reported that various useful polymers can be synthesized
from 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural (HMF), the biomaterial used in this
study. A high yield of FDCA can be obtained when HMF is oxidized in a
diluted solution under 2 weight percentage (wt%) with various supported
metal catalysts.
However, a major stumbling block to industrial application lies with the
use of a concentrated solution of 10-20 wt%, which is essential for
efficient and scalable production of FDCA in the chemical industry. When
HMF was simply oxidized in a concentrated solution (10 wt%), the FDCA
yield was only around 30%, and a large amount of solid by-products was
formed simultaneously. This is due to complex side reactions induced
from HMF itself.
Producing FDCA with High Yields
In the study published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition, a Japan-Netherland research team led by Associate Professor Kiyotaka Nakajima at Hokkaido University and Professor Emiel J.M. Hensen at Eindhove University of Technology succeeded in suppressing the side reactions and producing FDCA with high yields from concentrated HMF solutions (10~20 wt%) without by-products formation. Specifically, they first acetalized HMF with 1,3-propanediol to protect by-product-inducing formyl groups and then oxidized HMF-acetal with a supported Au catalyst.
Conventional methods produce by-products making large-scale FDCA production difficult, while this new method yields FDCA efficiently without by-products formation.
Producing Chemicals from Sugar-based Biomaterials
About 80% of 1,3-propanediol used to protect formyl groups can be reused for the subsequent reactions. In addition, drastic improvement in the substrate concentration reduces the amount of solvents used in the production process.
Kiyotaka Nakajima says “It is significant that our method can reduce the total energy consumption required for complex work-up processes to isolate the reaction product.”
“These results represent a significant advance over the current state of the art, overcoming an inherent limitation of the oxidation of HMF to an important monomer for biopolymer production. Controlling the reactivity of formyl group could open the door for the production of commodity chemicals from sugar-based biomaterials,” says Kiyotaka Nakajima. This study was conducted jointly with Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation.
Source: Hokkaido University
Tuesday, December 18, 2018
U.S. DOT approves high-pressure vessel hydrogen transport systems
Hexagon Composites has received a special permit from the United
States Department of Transportation (DOT) for the highest pressure gas
transport systems ever. The permit authorizes the manufacture, marking,
sale and use of Hexagon’s 500 and 950 bar cylinders for over-the-road
transport modules in the United States, for hydrogen and other gases.
“The DOT permit is a milestone for the hydrogen refueling market where higher pressures are sought to move more hydrogen per trailer trip, which in turn reduces the overall price of hydrogen fuel at the pump,” said Hartmut Fehrenbach, Vice President of Hydrogen Distribution of Hexagon. “This represents a key step to accelerate the ongoing adoption of fuel cell vehicles and transformation to a zero-emission and domestically sourced energy landscape.”
Hexagon is the first manufacturer to receive U.S. DOT special permit (SP20391) for 950 bar (13,775 psig). Being able to move 950 bar pressure vessel systems over the road enables the implementation of mobile hydrogen refueling units for fuel cell vehicles using 700 bar on-board storage tanks. Mobile refueling units strengthen the expanding hydrogen refueling network before permanent stations can be established.
Hexagon is designing transport systems for hydrogen for the United States, building on their experience and success with hydrogen transport modules already in use with European distribution customers and Mobile Pipeline® transportation modules in use globally with natural gas distribution customers.
Source: Hexagon
“The DOT permit is a milestone for the hydrogen refueling market where higher pressures are sought to move more hydrogen per trailer trip, which in turn reduces the overall price of hydrogen fuel at the pump,” said Hartmut Fehrenbach, Vice President of Hydrogen Distribution of Hexagon. “This represents a key step to accelerate the ongoing adoption of fuel cell vehicles and transformation to a zero-emission and domestically sourced energy landscape.”
Hexagon is the first manufacturer to receive U.S. DOT special permit (SP20391) for 950 bar (13,775 psig). Being able to move 950 bar pressure vessel systems over the road enables the implementation of mobile hydrogen refueling units for fuel cell vehicles using 700 bar on-board storage tanks. Mobile refueling units strengthen the expanding hydrogen refueling network before permanent stations can be established.
Hexagon is designing transport systems for hydrogen for the United States, building on their experience and success with hydrogen transport modules already in use with European distribution customers and Mobile Pipeline® transportation modules in use globally with natural gas distribution customers.
Source: Hexagon
Evonik Offers Methacrylate Monomer with Flame Retardant & Anti-corrosive Properties
Evonik has planned to market 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate phosphate as an anti-corrosion agent and flame retardant under the brand name VISIOMER® HEMA-P 70M. Typical product applications of this methacrylate monomer include adhesives and plastics, paints and coatings, fibers, composite resins, and gel coats.
New Options Open for Customers with VISIOMER
Customers mainly use VISIOMER® HEMA-P 70M as an adhesion promoter, but the latest findings have also shown it to be an effective halogen-free, reactive flame retardant or anti-corrosion agent.
Since the substance serves as a reactive diluent or as a co-monomer bonded within the polymer backbone, it does not migrate like conventional flame retardants. VISIOMER® HEMA-P 70M further improves flame retardancy in combination with non-polymerizable flame retardants.
“VISIOMER® HEMA-P 70M offers new options for customers with special requirements for flame-retardant and anti-corrosion properties. This monomer adds a specialty methacrylate with particular functionalities to Evonik’s portfolio and underscores our role as a solution provider for innovative customers,” says Dr. Martin Trocha, the head of Evonik’s Application Monomers Product Line.
VISIOMER® HEMA-P 70M is a highly versatile monomer that contains 30% methyl methacrylate and is particularly easy to process because of its low viscosity. Thanks to
its low color index, the specialty monomer is particularly well-suited for optical applications in acrylate and methacrylate systems. This enables the use in applications with high demands for transparency and surface quality, such as surface coatings, plastics or adhesives.
Moreover, the monomer protects against static charging and has an emulsion stabilizing effect.
Source: Evonik
Since the substance serves as a reactive diluent or as a co-monomer bonded within the polymer backbone, it does not migrate like conventional flame retardants. VISIOMER® HEMA-P 70M further improves flame retardancy in combination with non-polymerizable flame retardants.
“VISIOMER® HEMA-P 70M offers new options for customers with special requirements for flame-retardant and anti-corrosion properties. This monomer adds a specialty methacrylate with particular functionalities to Evonik’s portfolio and underscores our role as a solution provider for innovative customers,” says Dr. Martin Trocha, the head of Evonik’s Application Monomers Product Line.
Ease of Process with Low Viscosity
VISIOMER® HEMA-P 70M is a highly versatile monomer that contains 30% methyl methacrylate and is particularly easy to process because of its low viscosity. Thanks to
its low color index, the specialty monomer is particularly well-suited for optical applications in acrylate and methacrylate systems. This enables the use in applications with high demands for transparency and surface quality, such as surface coatings, plastics or adhesives.
Moreover, the monomer protects against static charging and has an emulsion stabilizing effect.
Source: Evonik
Sunday, December 16, 2018
Circa Receives ECHA Approval for Bio-based Di-polar Solvent Manufacture
Circa Group has received authorization from the European Chemicals
Agency (ECHA) to manufacture or import up to 100 tones/year of its
bio-based solvent Cyrene™ in the European Union, after receiving REACH
Annex VIII approval.
A chiral dipolar aprotic solvent, Cyrene™ was developed in conjunction
with the Green Chemistry Centre of Excellence (GCCE) at the University
of York. Cyrene™ is a two-step conversion of waste biomass, produced at
Circa's large-scale prototype plant, built in partnership with pulp and
paper company Norske Skog in Tasmania, Australia.
Solvent regulation is increasingly focused on restricting hazardous chemicals to manage their risk to people animals and the environment. In the EU, widely used solvents such as NMP, DMF and DMAc are on the candidate list of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) due to their reprotoxicity.
In addition, a new restriction on NMP was adopted earlier this year, meaning that after May 2020, use will be further restricted and it will not be able to be manufactured or used in the EU unless operational conditions are maintained to ensure that exposure to workers is below specified levels.
Tony Duncan, CEO and co-founder of Circa Group, said, "Annex VIII authorization is a major milestone for Cyrene™ and we are delighted to have been given the go-ahead to sell Cyrene™ in significantly larger quantities in Europe.
Safer solvents are urgently required and with Cyrene™, we are also offering a bio-based solution with a unique property set, including viscosity, surface tension and polarities – making it an exciting new prospect for advanced materials. Our next goal is registration of Cyrene™ in the US and other jurisdictions will soon follow.”
Source: Circa
Cyrene™ : An Alternative to Polar Aprotic Solvents
A chiral dipolar aprotic solvent, Cyrene™ was developed in conjunction
with the Green Chemistry Centre of Excellence (GCCE) at the University
of York. Cyrene™ is a two-step conversion of waste biomass, produced at
Circa's large-scale prototype plant, built in partnership with pulp and
paper company Norske Skog in Tasmania, Australia.
Cyrene™ provides a safer alternative to these polar aprotic solvents
facing regulatory pressure worldwide and is available through Circa’s
distributors Merck/Sigma and Will&Co.
Restricting the Possible Toxic Solvents
Solvent regulation is increasingly focused on restricting hazardous chemicals to manage their risk to people animals and the environment. In the EU, widely used solvents such as NMP, DMF and DMAc are on the candidate list of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) due to their reprotoxicity.
In addition, a new restriction on NMP was adopted earlier this year, meaning that after May 2020, use will be further restricted and it will not be able to be manufactured or used in the EU unless operational conditions are maintained to ensure that exposure to workers is below specified levels.
Crossing a Major Milestone
Tony Duncan, CEO and co-founder of Circa Group, said, "Annex VIII authorization is a major milestone for Cyrene™ and we are delighted to have been given the go-ahead to sell Cyrene™ in significantly larger quantities in Europe.
Safer solvents are urgently required and with Cyrene™, we are also offering a bio-based solution with a unique property set, including viscosity, surface tension and polarities – making it an exciting new prospect for advanced materials. Our next goal is registration of Cyrene™ in the US and other jurisdictions will soon follow.”
Source: Circa
Tuesday, December 11, 2018
Sulzer Enters into Partnership to Promote PLA-based Sustainable Plastics Production
Futerro, Sulzer and TechnipFMC team up to simplify the manufacture of bioplastics.
Three major process technology and equipment specialists, Futerro,
Sulzer and TechnipFMC, have formed the PLAnet™ initiative in equal
partnership to promote the production of sustainable plastics made of Poly-Lactic Acid (PLA).
The strategic collaboration will support manufacturers interested in
entering the bioplastic market by delivering integrated PLA technology
packages.
PLA is a versatile bio-based and biodegradable polymer that can replace petroleum-based plastics in a wide range of applications. Different stages are required to convert sugars from crops into lactic acid, lactide and subsequently PLA.
The agreement between the three parties offers to agricultural, chemical
and fiber industries, a fully integrated package addressing the whole
PLA value chain. In this way, customers can benefit from direct access
to state-of-the-art, customizable solutions for all the aspects and
stages of PLA production. PLAnet™ offers the possibility of a “one-stop
shop” for customers interested in PLA production by providing a single
point of contact and responsibility.
In particular, PLAnet™ supports the construction of plants of any size, including PLA facilities with a throughput of up to 100’000 tons per year - that permit manufacturers to save both capital expenditures (CAPEX) and operating expenses (OPEX) by providing for integrated and optimized plant section design.
Within the PLAnet™ partnership, Futerro’s proprietary technology focuses on the production of lactic acid and raw lactide from sugar or, directly, from biomass; Sulzer contributes the process for the purification of lactide and its polymerization to obtain PLA while TechnipFMC acts as technology integrator to deliver seamless and optimized Front-End Engineering Design (FEED) packages.
The promotion of greener alternatives to traditional plastics needs to be backed by suitable technologies that enable the industry to produce high-quality bioplastics in an efficient manner. This can be made possible via the PLAnet™ partnership between Futerro, Sulzer and TechnipFMC by leveraging their world-leading technologies, expertise and skills for the entire PLA value chain.
Source: Sulzer
PLA is a versatile bio-based and biodegradable polymer that can replace petroleum-based plastics in a wide range of applications. Different stages are required to convert sugars from crops into lactic acid, lactide and subsequently PLA.
Facilitating Bioplastics Production
Futerro, a well-established technology provider for lactic acid and lactide production, and Sulzer Chemtech, a leading specialist in separation and mixing technologies have over 25 years of experience in lactic acid and PLA’s related processes. Together they have further shown their commitment to facilitate the production of bioplastics by establishing a partnership with TechnipFMC, a leading global EPC contractor with experience in technology development and licensing with fast growing activities in bioplastics and green chemicals.PLAnet™ Initiative
The agreement between the three parties offers to agricultural, chemical
and fiber industries, a fully integrated package addressing the whole
PLA value chain. In this way, customers can benefit from direct access
to state-of-the-art, customizable solutions for all the aspects and
stages of PLA production. PLAnet™ offers the possibility of a “one-stop
shop” for customers interested in PLA production by providing a single
point of contact and responsibility.
Goal of PLAnet™
In particular, PLAnet™ supports the construction of plants of any size, including PLA facilities with a throughput of up to 100’000 tons per year - that permit manufacturers to save both capital expenditures (CAPEX) and operating expenses (OPEX) by providing for integrated and optimized plant section design.
Within the PLAnet™ partnership, Futerro’s proprietary technology focuses on the production of lactic acid and raw lactide from sugar or, directly, from biomass; Sulzer contributes the process for the purification of lactide and its polymerization to obtain PLA while TechnipFMC acts as technology integrator to deliver seamless and optimized Front-End Engineering Design (FEED) packages.
The promotion of greener alternatives to traditional plastics needs to be backed by suitable technologies that enable the industry to produce high-quality bioplastics in an efficient manner. This can be made possible via the PLAnet™ partnership between Futerro, Sulzer and TechnipFMC by leveraging their world-leading technologies, expertise and skills for the entire PLA value chain.
Source: Sulzer
Saturday, December 8, 2018
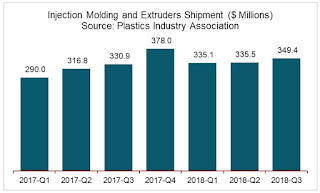
Plastics Machinery Shipments Continued to Increase in Q3 of 2018 in North America
The plastics machinery shipments in North America continued to increase in the third quarter according to the statistics compiled and reported by the Plastics Industry Association’s (PLASTICS) Committee on Equipment Statistics (CES).
Injection Molding & Extrusion Machinery Shipment
The preliminary estimate of shipments of primary plastics equipment (injection molding and extrusion) for reporting companies totaled $349.4 million in the third quarter. This was a 4.1-percent increase from the $335.5 million (revised) second-quarter shipment. Injection molding shipments in the second quarter were higher than previously thought. Year over year, shipments grew 5.6 percent.
Perc Pineda PhD, Chief Economist of PLASTICS, said:
“Plastics machinery shipments recovered in the third quarter following a weak second quarter. We expect higher shipments in the fourth quarter. We have a tight labor market and U.S. manufacturers, including plastics machinery manufacturers, have been working on production backlogs. As a result, shipments are pushed into the next quarters.”
Quarterly Statistics
- On a quarterly basis, injection molding shipments increased 2.1 percent. Single-screw and twin-screw extruder shipments continued double-digit growth of 23.8 percent and 14.2 percent, respectively.
- Compared to the third quarter last year, shipments of injection molding were up 4.6 percent. Shipments of single-screw extruders rose 7.7 percent and twin-screw extruders 17.2 percent over the same period.
Perc Pineda said:
“Except for soft auto and home sales numbers in the third quarter, the U.S. economy is still in expansionary mode—and that’s good news for plastics machinery manufacturing. While there are projections of moderate growth next year, it is expected that the U.S. economy will remain healthy.”
Source: Plastics Industry Association (PLASTICS)
Friday, December 7, 2018
California Bans Sale of Upholstered Products Containing FRs Above 1000ppm
California has joined states to ban flame retardants in certain
household products. Starting January 1, 2020, it will be prohibited to
sell or distribute children’s products, mattresses, and upholstered
furniture that contain flame retardants in concentrations above 1,000
parts per million (ppm) in the state of California.
In passing the bill, the Legislature cited proof that flame retardants
do little to increase fire safety, and expressed concerns about the link
between flame retardants and various health problems, such as
developmental problems in children and cancer.
The Bureau of Electronic and Appliance Repair, Home Furnishings, and Thermal Insulation is sanctioned to enforce the new law and adopt implementing rules and regulations.
California is one of a number of states that have banned flame retardants or specific chemicals commonly used in FRs.
Source: SpecialChem
Link Between Flame Retardants and Various Health Problems
In passing the bill, the Legislature cited proof that flame retardants
do little to increase fire safety, and expressed concerns about the link
between flame retardants and various health problems, such as
developmental problems in children and cancer.
Implementing Rules and Regulations
The law needs the International Sleep Products Association to survey mattress producers every three years to determine what materials are being used to meet flammability standards.The Bureau of Electronic and Appliance Repair, Home Furnishings, and Thermal Insulation is sanctioned to enforce the new law and adopt implementing rules and regulations.
California is one of a number of states that have banned flame retardants or specific chemicals commonly used in FRs.
San Francisco’s Flame Retardant Ban to Take Effect
- On January 1, 2019, San Francisco’s similar ban on sale of upholstered furniture and juvenile products containing flame retardants goes into effect
- From next year, it will be prohibited to sell upholstered furniture, reupholstered furniture, or juvenile products which have been made with, or contain a flame retardant chemical at a level above 1, 000 parts per million.
- The same ban goes into effect on July 1, 2019 for similar products that have electrical or electronic components.
Labeling Requirements
- In addition to banning the sale of products with added flame retardants, the San Francisco ordinance includes labeling requirements for all upholstered furniture and children’s products sold in the city.
- The products must be affixed with labels that state that the item does not contain the flame retardants.
- The labels required by San Francisco’s ordinance are the same as those currently required under California’s SB 1019, but the label must be marked to indicate that the upholstery materials contain NO added flame retardant chemicals.
Penalties for Violation
Penalties for violation of the ordinance may not exceed $1,000 per day per violation, with each day constituting a separate violation, and each product for sale also constituting a separate violation. In determining the appropriate penalty, the Director or the court will consider “the extent of harm caused by the violation, the nature and persistence of the violation, the frequency of past violations, any action taken to mitigate the violation, and the financial burden to the violator.”Source: SpecialChem
Wednesday, December 5, 2018
Teknor Apex’s New Medical-grade TPEs Replace Silicone in Biopharmaceutical Tubing
Three new medical-grade thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) for
biopharmaceutical tubing provide performance superior to the industry
standard TPE in this application, making them effective alternatives to
widely used silicone.
Teknor Apex Company will introduce the new Medalist® compounds at MD&M West (Booth 2015) and will make a presentation on grades for peristaltic pump applications at the “Tech Theater” during the show. The presentation is scheduled for 1:30 pm on Wednesday, February 6.
Teknor Apex recommends three compounds for challenging tubing applications in the biopharma industry for peristaltic pumps and extreme low temperature applications. The materials designed for peristaltic pump tubing provide the elasticity required to keep pace with rapid pump action and the durability needed for the tubing to retain its shape and remain intact over time. In comparison with the industry-standard TPE alternative to silicone, the Medalist TPEs exhibit lower levels of spallation—the shedding of particles from the inner and outer surfaces of the tubing caused by repeated compression and release during pump operation.
• Medalist MD-12352 is a 52 Shore A translucent TPE designed for peristaltic pump tubing.
The new Medalist compounds are made with FDA-listed ingredients, are certified at a minimum to the ISO 10993-5 standard for biocompatibility, and are REACH SVHC compliant. They are free of DEHP and other phthalates, BPA, and latex. Standard grades are ADM-free.
Source: Teknor Apex Company
Teknor Apex Company will introduce the new Medalist® compounds at MD&M West (Booth 2015) and will make a presentation on grades for peristaltic pump applications at the “Tech Theater” during the show. The presentation is scheduled for 1:30 pm on Wednesday, February 6.
Clear & Translucent Medalist® Medical TPEs
Teknor Apex recommends three compounds for challenging tubing applications in the biopharma industry for peristaltic pumps and extreme low temperature applications. The materials designed for peristaltic pump tubing provide the elasticity required to keep pace with rapid pump action and the durability needed for the tubing to retain its shape and remain intact over time. In comparison with the industry-standard TPE alternative to silicone, the Medalist TPEs exhibit lower levels of spallation—the shedding of particles from the inner and outer surfaces of the tubing caused by repeated compression and release during pump operation.
Three New Medalist® Compounds
• Medalist MD-12352 is a 52 Shore A translucent TPE designed for peristaltic pump tubing.
• Medalist MD-50357 is a clear, slightly harder TPE (58 Shore A) for peristaltic pump tubing, which can be sterile welded and heat sealed.
• Medalist MD-10353
is a clear compound used in biopharma tubing in extreme low temperature
applications. With a brittleness temperature below -60° C, this TPE can
be used for tubing that remains flexible and elastic, facilitating
fluid transfer in the manufacturing process of heat-sensitive
biopharmaceuticals.
These three Medalist compounds exhibit significantly lower permeability
than silicones. They can be sterilized by means of e-beam, gamma
irradiation, and ethylene oxide (EtO).
Ross van Royen, senior market manager of regulated products, said:
“At a time when silicones are in short supply, Teknor Apex can
provide an assured global supply chain for all Medalist TPEs, producing
them at ISO-13485-certified facilities in the U.S, and Singapore. As
alternatives to silicone, our three new Medalist compounds provide
better performance than the industry-standard TPE used thus far.”
Certifications & Compliance
The new Medalist compounds are made with FDA-listed ingredients, are certified at a minimum to the ISO 10993-5 standard for biocompatibility, and are REACH SVHC compliant. They are free of DEHP and other phthalates, BPA, and latex. Standard grades are ADM-free.
Source: Teknor Apex Company
Tuesday, December 4, 2018
Scientists to combine ultrasonic, vibration and heat for flaw detection in aviation
Daria Derusova, JRF from the TPU Research School of High Energy
Physics is developing a system combining three methods of
non-destructive testing including a vibrational, resonant ultrasonic and
thermal ones to test composites for aviation applications.
This approach is of interest for aviation and automobile industries as it will make it possible to monitor the quality of complex and large-sized products made of composite materials taking into account their physical properties. The Russian Science Foundation has supported this two-year project up to 2020.
The project manager Daria Derusova says ‘Every year, new composite materials appear and they challenge existing methods of non-destructive testing. Joints between the materials are of particular complexity and importance.’
Now classic ultrasonic and X-ray testing are used at the production.
The latter is the most accurate but it does not fit to large-sized objects that are presented in aviation a lot. In turn, ultrasonic facilities consume kilowatts of electricity to stimulate materials with a mono-frequency acoustic signal. Laser vibrometry in the combination with resonant stimulation of defects is seen as the most promising modern method. Such an approach allows activating local resonant vibration in the area of damage that also causes the increase of temperature in this area. In turn, an infrared camera will allow the registration of the temperature change and the addition of data about the quality of products. As a result, we expect to build a laboratory facility to test large and complex objects by form.
Meantime, it will consume several times less electricity than high-power ultrasonic installations. The developed approach will be an alternative to the existing methods of non-destructive testing in aviation and machine-building industry,’ says the early-career researcher.
The facility will comprise of such elements as resonant ultrasonic stimulation using piezoelectric transducers, a scanning laser Doppler vibrometer and an infrared camera with specialized software.
‘The essence of the system is that a tested object – material is exposed to acoustic stimulation in a wide range of frequencies.
Elastic waves create vibrations of both material itself and its inhomogeneities. The resonant frequency of vibrations of defects’ walls differs from that of the object that can be detected with a scanning vibrometer. In addition, due to intense resonant vibrations defect areas are locally heated. We register these changes with an infrared camera. The data of quality testing allow us to identify a defect itself, its location, form, and size,’ clarifies Daria Derusova.
In the framework of this project, TPU scientists cooperate with peers from the Institute of Strength Physics and Materials Science SB RAS (Laboratory for Quality Testing of Materials and Structures), the University of L'Aquila (Italy) and the Symbiosis Institute of Technology (India). The S.А. Chaplygin Siberian Research Institute of Aviation (SibNIA, Novosibirsk) provides samples of materials for testing proposed technology.
Source: www.tpu.ru
This approach is of interest for aviation and automobile industries as it will make it possible to monitor the quality of complex and large-sized products made of composite materials taking into account their physical properties. The Russian Science Foundation has supported this two-year project up to 2020.
The project manager Daria Derusova says ‘Every year, new composite materials appear and they challenge existing methods of non-destructive testing. Joints between the materials are of particular complexity and importance.’
Now classic ultrasonic and X-ray testing are used at the production.
The latter is the most accurate but it does not fit to large-sized objects that are presented in aviation a lot. In turn, ultrasonic facilities consume kilowatts of electricity to stimulate materials with a mono-frequency acoustic signal. Laser vibrometry in the combination with resonant stimulation of defects is seen as the most promising modern method. Such an approach allows activating local resonant vibration in the area of damage that also causes the increase of temperature in this area. In turn, an infrared camera will allow the registration of the temperature change and the addition of data about the quality of products. As a result, we expect to build a laboratory facility to test large and complex objects by form.
Meantime, it will consume several times less electricity than high-power ultrasonic installations. The developed approach will be an alternative to the existing methods of non-destructive testing in aviation and machine-building industry,’ says the early-career researcher.
The facility will comprise of such elements as resonant ultrasonic stimulation using piezoelectric transducers, a scanning laser Doppler vibrometer and an infrared camera with specialized software.
‘The essence of the system is that a tested object – material is exposed to acoustic stimulation in a wide range of frequencies.
Elastic waves create vibrations of both material itself and its inhomogeneities. The resonant frequency of vibrations of defects’ walls differs from that of the object that can be detected with a scanning vibrometer. In addition, due to intense resonant vibrations defect areas are locally heated. We register these changes with an infrared camera. The data of quality testing allow us to identify a defect itself, its location, form, and size,’ clarifies Daria Derusova.
In the framework of this project, TPU scientists cooperate with peers from the Institute of Strength Physics and Materials Science SB RAS (Laboratory for Quality Testing of Materials and Structures), the University of L'Aquila (Italy) and the Symbiosis Institute of Technology (India). The S.А. Chaplygin Siberian Research Institute of Aviation (SibNIA, Novosibirsk) provides samples of materials for testing proposed technology.
Source: www.tpu.ru
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
DEMGY will be present at JEC World 2026 - March 10–12, 2026, Paris‑Nord Villepinte
Once again this year, DEMGY Group, world leader in aircraft interiors, invites you to join us at , the must-attend global event for composit...

-
Today's KNOWLEDGE Share What Is Going Wrong in UK Plastics Recycling? Biffa shut its Sunderland plant. Viridor walked away from Avonmout...
-
Today's KNOWLEDGE Share “Robotic 3D printing can compete with traditional boatbuilding”, Simone Barbera and Mattia De Santis, Caracol V...
-
Borealis is proud to announce that its new compounding line for recyclate-based polyolefins (rPO) is now fully operational in Beringen, Bel...












Nanotubes create new business opportunities for conductive PVC plastisol manufacturers. They enjoy an overwhelming welcome in the mining industry, where assurance of safety is vital. Here are a few examples of graphene nanotubes blazing their own trail in this market. 0.4–0.5 wt.% graphene nanotube concentrate in PVC plastisol-based flexible ventilation ducting and fiberglass mesh for mining applications enable manufacturers to obtain a resistivity of 107 Ω/sq with maintained mechanical performance. PVC plastisol-based anti-static textiles and treadmill belts mapping out graphene nanotubes extensive application in industry. Uniform, permanent, stable and humidity-independent electrical conductivity – all guaranteed by graphene nanotubes.